Enabling Greater Transparency, Accountability and Participation in Nigeria
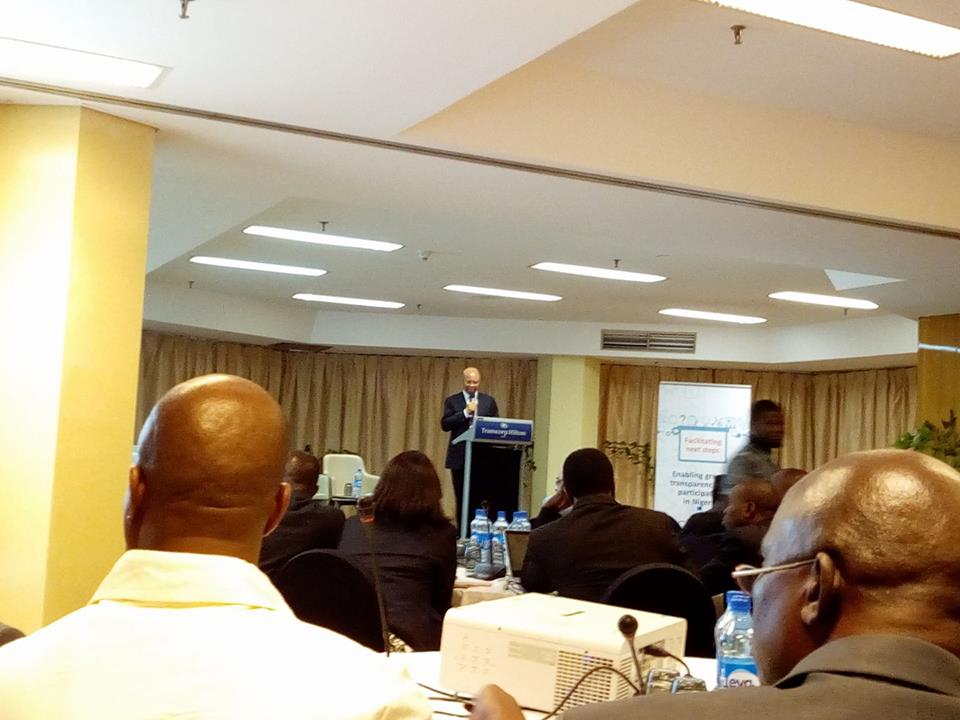
[The DG of Budget Office, Ben Akabueze making a presentation during the Budget Transparency and Accountability Workshop]
It is widely accepted that transparency in government leads to the generation of government accountability since it allows citizens of a democracy to reduce government corruption, bribery and other malfeasance, and control their government. It is also widely accepted that an open, transparent government allows for the dissemination of information and proceedings of government, which in turn forces government to be accountable, helps to guarantee societal progress and effective public oversight, while ensuring participation.
There have been several transparency, accountability and participation movements all over the world. Such movements in developing countries have more justifications for clamouring for such as a result of poor governance, systemic wrecking of public funds, public records inaccessibility and impecunious citizen participation in governance. As a result, citizens of such countries have found it increasingly difficult to hold their governments to account.
This is the case of Nigeria, where several non-profits and movements have been pushing for greater governmental accountability and transparency. And for the first time since the history of the country, the present administration made a striking commitment by signing unto the Open Government Partnership (OGP). The OGP is a multilateral and multi-stakeholder initiative that aims to secure concrete commitments from national governments to promote transparency, empower citizens, harness new technologies to strengthen governance and fight corruption. Nigeria getting on-board the partnership through President Buhari’s commitment to such resulted in a synthesis of government and civil society efforts to realize open government in the country.
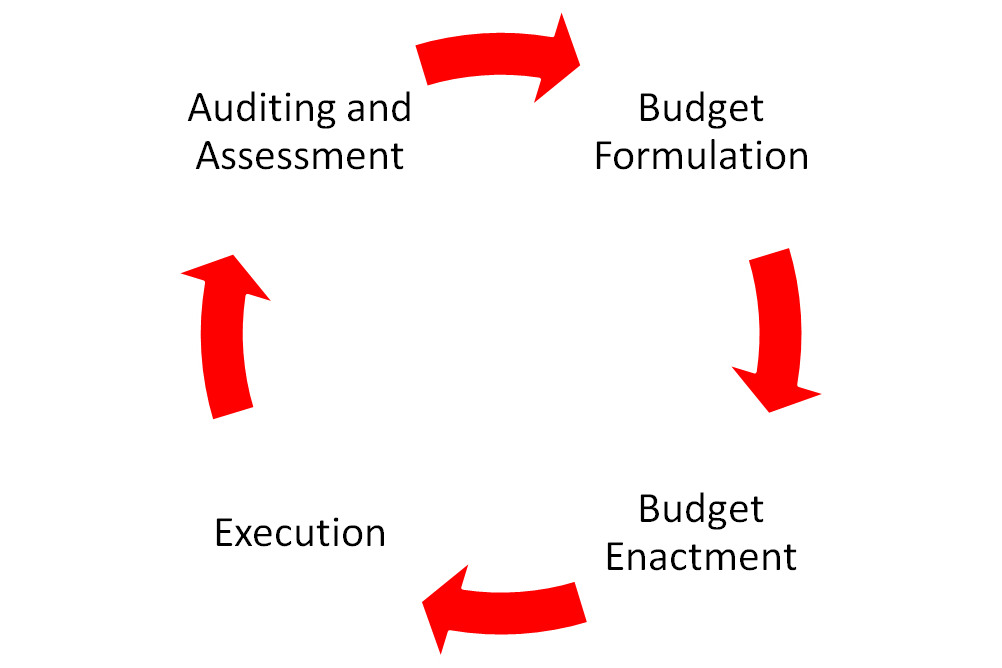
Currently, Nigeria just started implementing the National Action Plan (NAP), a key process of the OGP. The plan has 4 commitments that both the government and civil society have made and are implementing across ensuring fiscal transparency, fighting corruption, improving citizenry access to information and citizen engagement.
In line with these developments, the Budget Office of the Federation (BoF) and the Collaborative Africa Budget Reform Initiative organized a workshop on budget transparency and accountability on 9 May 2017 at Transcorp Hilton Hotels, Abuja. In attendance were several international and domestic stakeholders from the government, civil society and private sector. The workshop was organized to allow the Nigerian government examine how it can bolster transparency and participation outcomes in the country with focus on budget transparency – how budget information can be made more accessible, how to move forward in implementing reforms that improves Nigeria’s Open Budget Index Score (OBIS).
The workshop majorly kicked off through a presentation by the Director-General of BoF on Transparency, Accountability and Participation: Reforms and Why It Matters. He used his presentation to highlight progresses made on open government in the country, detailing the OGP and its NAP Commitments. He also mentioned that an area that requires commitments and attention of all relevant stakeholders is Nigeria’s OBIS which as at 2015 was at number 24 on the ranking under insufficient. He also mentioned that in a bid to counter such embarrassing trend, the BoF is on the verge of commissioning the Citizen’s Budget Portal where citizens would have timely information of budget processes including contracting and implementation. In addition, the portal will have further contents such as the BoF Help Desk and Hot Lines to take questions from the general public on budget issues and implementation.
This was followed by a presentation by Atiku Samuel of BudgIT on the Status of Budget Transparency in Nigeria. He took his time to explain the international standards of budget transparency and how the OBIS is measured. After this was a session on How to Make Budget Data More Accessible by Atzimba Baltazar of COMETA. She emphasised the need for a Citizen’s budget which should be a few paged document on governmental revenues, debts and expenditure in a fiscal year using infographics and cartoons to simplify understanding for the citizenry. She lifted lessons Nigeria could learn from countries such as Tanzania, Kenya and South Africa where citizen’s budgets are already been issued out.
The last session was a group discussion on 3 key questions: 1). Do you have enough information on the budget? 2). Who do you go to access the information and 3). How do you prefer to access this information? The resolutions after the group discussions on the questions, respectively, are:
1). Yes, while we have information on the budget including the Medium Term Expenditure Framework, Budget Proposal, Appropriation Act, Budget Implementation Reports etc. the problem is that accessibility to these documents atimes are not timely. Most of them are not in open source formats. Most of the budget line items are not detailed enough, and ultimately, a lay man would not be able to understand the technicalities on most of these documents. 2). It was generally agreed that this should be from the Budget Office, Ministry of Finance and few other primarily concerned MDAs. 3). In open source format – the citizen’s budget and the citizen’s budget portal will go a long way in assisting in this regard.
While one must applaud the BoF and the present administration on efforts to use open government as a tool in fighting corruption, increasing participation and ensuring effective public oversight, there should be sufficient governmental political will in implementing the NAP, other consequent commitments and responding to Freedom of Information (FOI) Requests. For CODE (Follow The Money), the citizen’s budget portal will be largely utilitarian in accessing key budget information for rural communities which we fail to access on time even through piles of FOI requests. Such will enable us take such details down to rural communities and in building their capacity for effective public oversight, ensuring service delivery and in holding their governments accountable.
Chambers Umezulike is a Programme Manager at Connected Development and a Development Expert. He spends most of his time writing and choreographing researches on good and economic governance. He tweets via @Prof_Umezulike.